Scripting
Script for Detecting Keyboard Input
Keyboard input on the Peakboard Box can be detected using a script. An event is created, which is triggered with every key press. The event is linked to a function that decides which action to take based on specific inputs.
Detecting Keyboard Input
There are two types of keyboard input events that can be detected on the Peakboard Box: KeyPressed and KeyInput. The difference between these events is that KeyPressed is triggered with every key press, while KeyInput is only triggered when an input is completed with an Enter key.
The KeyPressed event is better suited for detecting key presses in real-time, as it triggers with every key press.
For text or number inputs that are completed with an Enter key, the KeyInput event is more appropriate, as it only triggers upon completed input.
Creating an Event
To create a KeyPressed or KeyInput event, add a new global event under Scripts in the Package Explorer. Right-click to open a context menu and select either KeyPressed or KeyInput event.
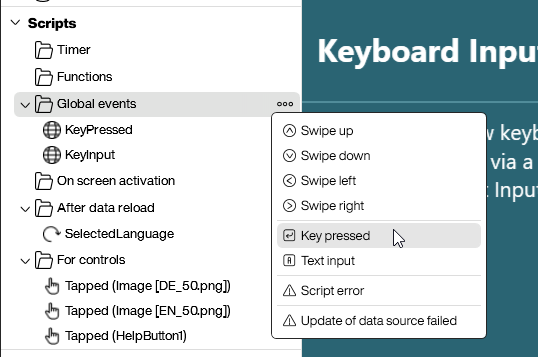
Once the event is created, you can define the script that will execute when a key press occurs.
Handling KeyPressed Events
Reading the Key Code
The key pressed can be accessed via the event parameter e. Using e.key returns the pressed key as a Key code.
e.key
It is important to note that this key code is a numeric value representing the key, not the letter value.
Converting Key Code to Letter
To obtain the letter value of the key, use the keytostring function. This function converts the numeric key code to the corresponding letter value.
keytostring(e.key)
Reacting to Keyboard Input
After converting the key code to a letter value, you can react to the input. An if statement can be used to check if the pressed key matches a specific value.
Here is an example that plays a buzzer sound if the A key was pressed:
if keytostring(e.key) == 'A' then
runtime.playsound('buzzer')
end
Detecting Modifier Keys
In addition to regular keys, modifier keys like Shift, Control, or Alt can also be detected. The modifiertostring function can be used to return the pressed modifier keys as a string.
Here is an example that checks if the Shift, Control, or Alt key is pressed and changes the background color of a control accordingly:
if string.contains(modifiertostring(e.modifier), 'Shift') then
screens['Screen1'].ShiftBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FFFFC400')
else
screens['Screen1'].ShiftBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FF2A6473')
end
if string.contains(modifiertostring(e.modifier), 'Control') then
screens['Screen1'].CtrlBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FFFFC400')
else
screens['Screen1'].CtrlBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FF2A6473')
end
if string.contains(modifiertostring(e.modifier), 'Alt') then
screens['Screen1'].AltBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FFFFC400')
else
screens['Screen1'].AltBg.background = brushes.fromhex('#FF2A6473')
end
Handling KeyInput Events
Unlike KeyPressed events, KeyInput events pass the entire text generated by the key presses. This text can then be processed further.
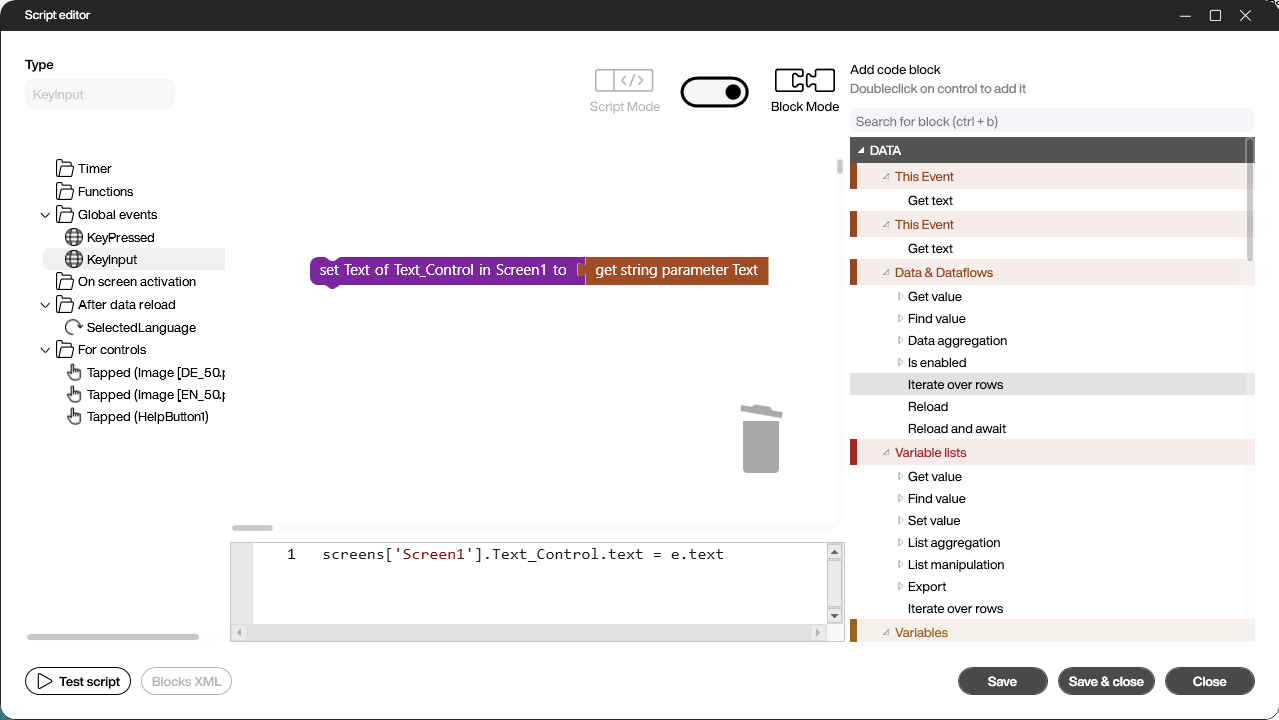
In the script, the text from the event can be read via the parameter e:
e.text
Responding to Keyboard Input
After the text has been read from the event, you can respond to the input. An if statement can be used to check if the entered text matches a specific value.
Here is an example that checks if the entered text is Hello:
if string.contains(e.text, 'Hello') then
runtime.playsound('buzzer')
end