Data sources
Azure IoT Hub
This article shows how to use the Azure IoT hub data source in Peakboard. Please first make the difference between the data sources IoT Hub and Event Hub clear. The latter is explained here. The event hub source is about receiving messages only. This is therefore only intended for asynchronous reaction to events. In the IoT hub source, the Peakboard acts as a device within the Azure IoT hub. It must be created there as a device. For this to work, you need the connection string from the Azure portal, which is directly associated with the device.
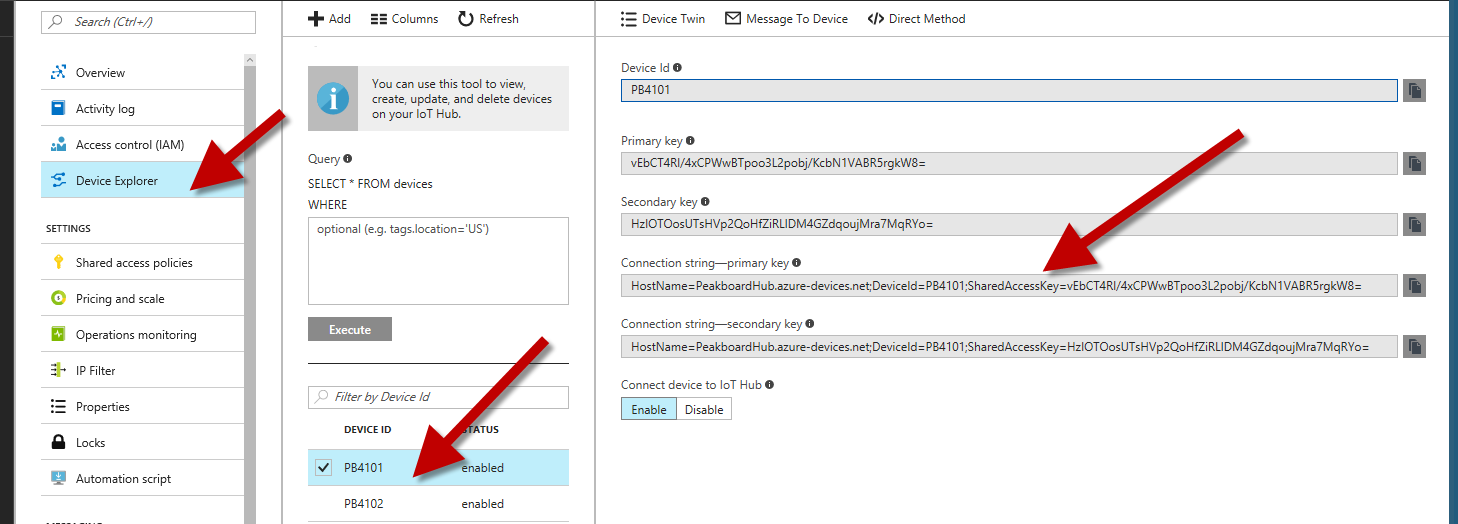
In order for the Peakboard to be able to do its job as a “device”, there are several communication channels which are explained below: Receive messages asynchronously, receive methods with return value synchronously and return a value, send messages from the Peakboard.
Receiving messages
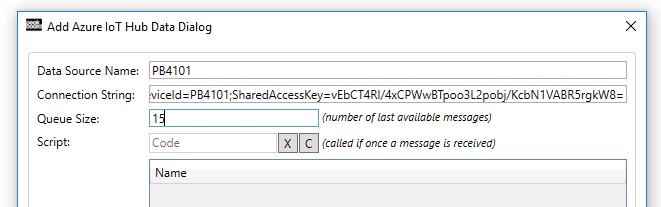
Incoming messages are stored in the data source in a table-like object with the three columns Timestamp, Topic and Text as you know it from a data source. The size of this queue can be set using a parameter. If you don’t value the content of the queue, you can also react to it with the help of a script. The script is simply called with every incoming message. The following example shows a script that simply writes the content of the message into a text field:
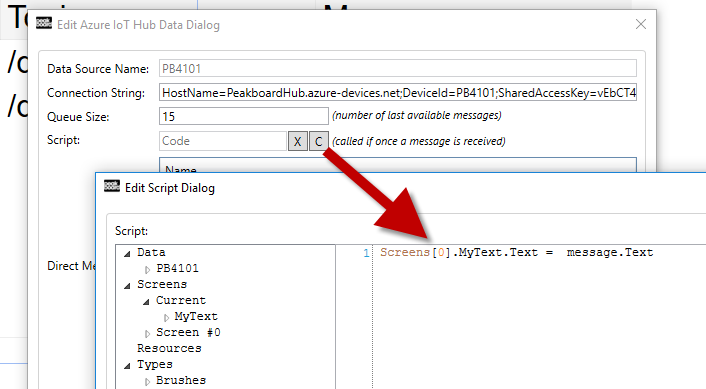
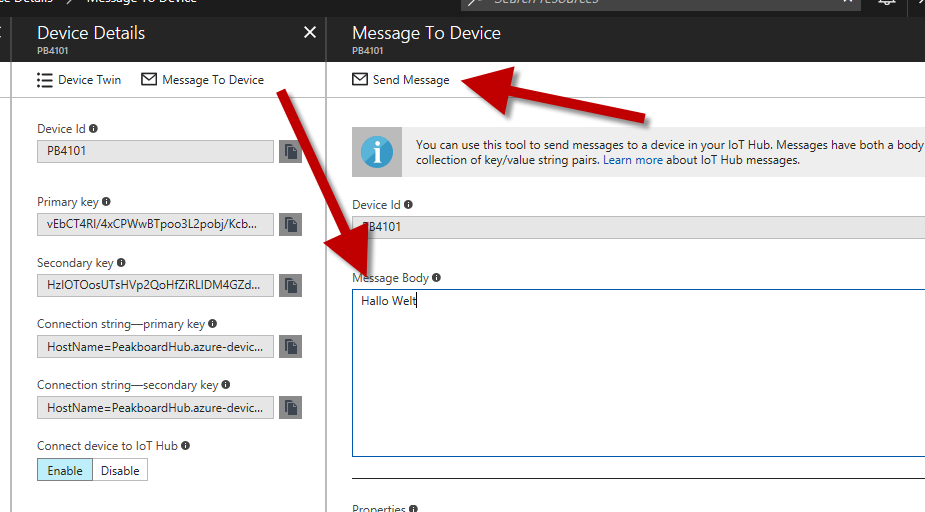
To send a test message, it is best to use the Azure test mode:
Receive and respond to methods
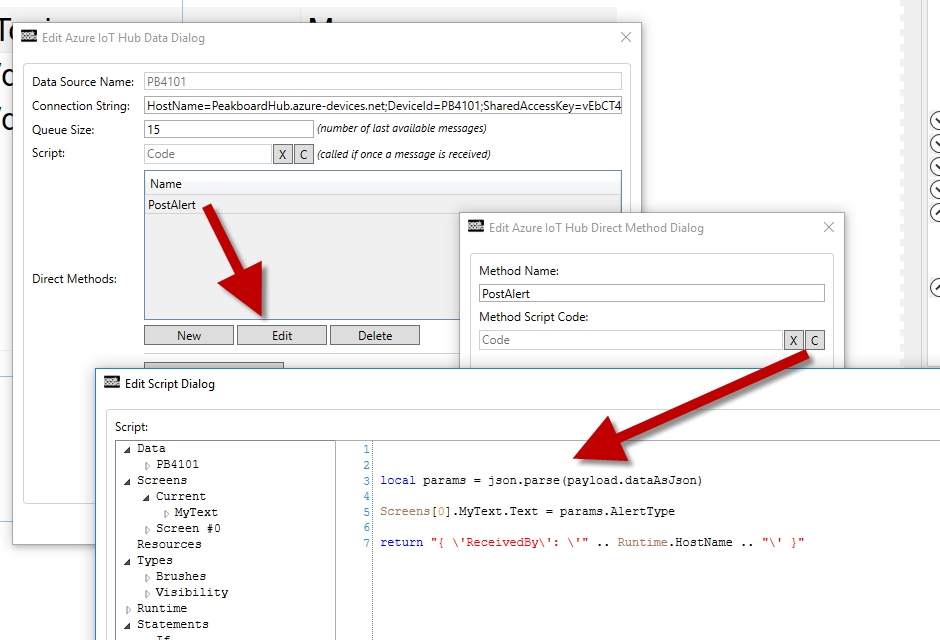
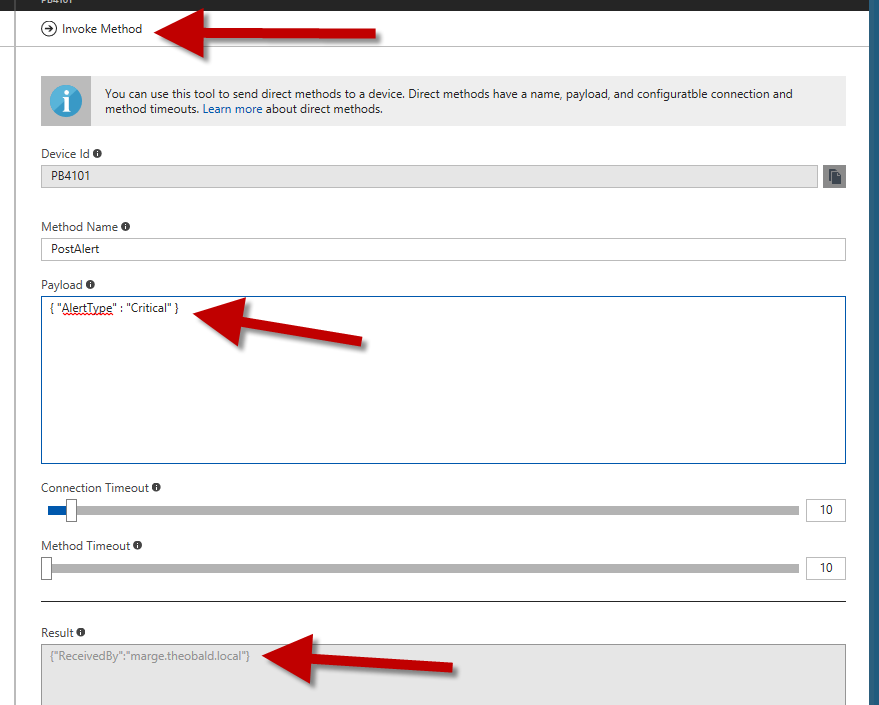
The second way of exchanging messages are methods. They differ from messages in that they have a return value. The device can therefore react to the message and return a kind of acknowledgement. An entry must be created in the method table for each method. The example shows the “PostAlert” method, which receives the message, evaluates it and returns the name of the Peakboard as JSON. Let’s assume that the method sends a JSON message with the type of alarm. The following screenshot shows how to create the request in the Azure method test dialog. You reach it like the test mode for messages (see above). The script code also shows how the JSON is parsed and processed correctly. The pure string can be reached via json.DataAsJson. The json.parse (…) function creates a dynamic object. The AlertType property is then accessed very easily.
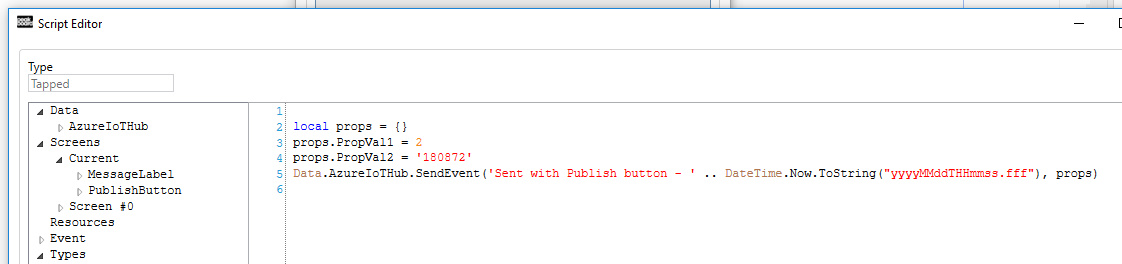
Sending messages from Peakboard to IoT Hub
The third and last aspect for using Peakboard as an IoT device is sending messages to the cloud. This can be done easily via a script. The following example is behind the tapped event of a button. The end user can thus send a message by pressing a button. Here too, a JSON string is typically sent again. You can see on the script how the JSON is formed from a dynamic object. The attributes are simply filled with values and created implicitly.