Data sources
External dynamic data sources illustrated by an XML data source example
Basically, Peakboard distinguishes between two main concepts of how dynamic content is embedded:
-
The data comes fully prepared from the external source and only needs to be integrated into a panel. This is the case, for example, if you integrate an external website in part or in entirety. Or even if you use a BI tool such as Power BI, QlikView, Tableau or similar and leave the preparation of the data to the BI tool. Peakboard then acts as a kind of display program and the respective pre-system takes care of the visual preparation.
-
The data comes in as raw data from an external source. Such sources can be, for example, XML, JSon, a database or a social media feed. Here, only the pure data is transported and the visualization then takes place directly in Peakboard. For this purpose, visual controls are available to display the data nicely, e.g. charts, tables, etc.
This guide deals exclusively with the second option. The basis will be an XML data source. Take a look at the following XML file. It contains all current departures from Stuttgart main station in real time and is provided by Deutsche Bahn:
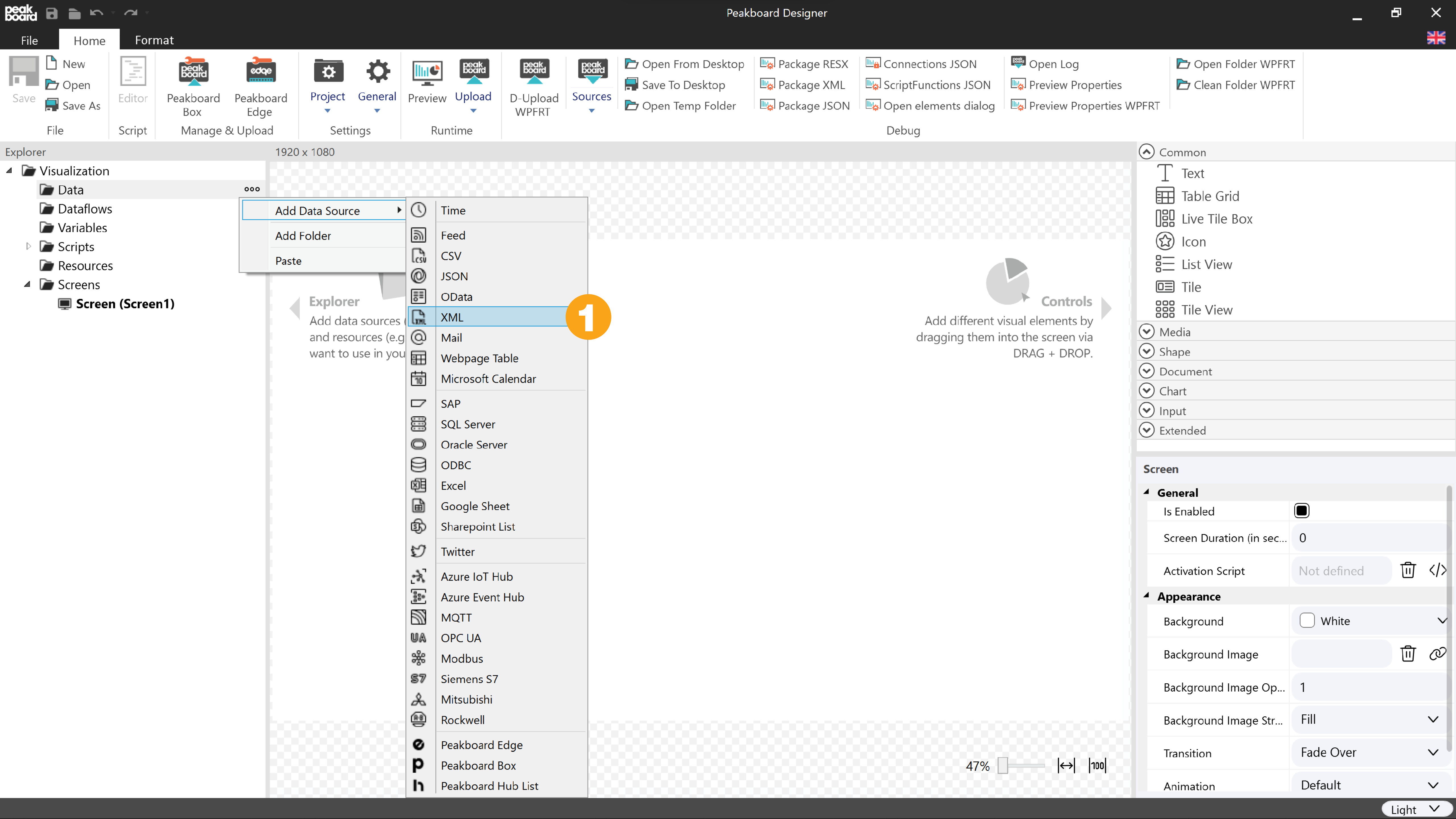
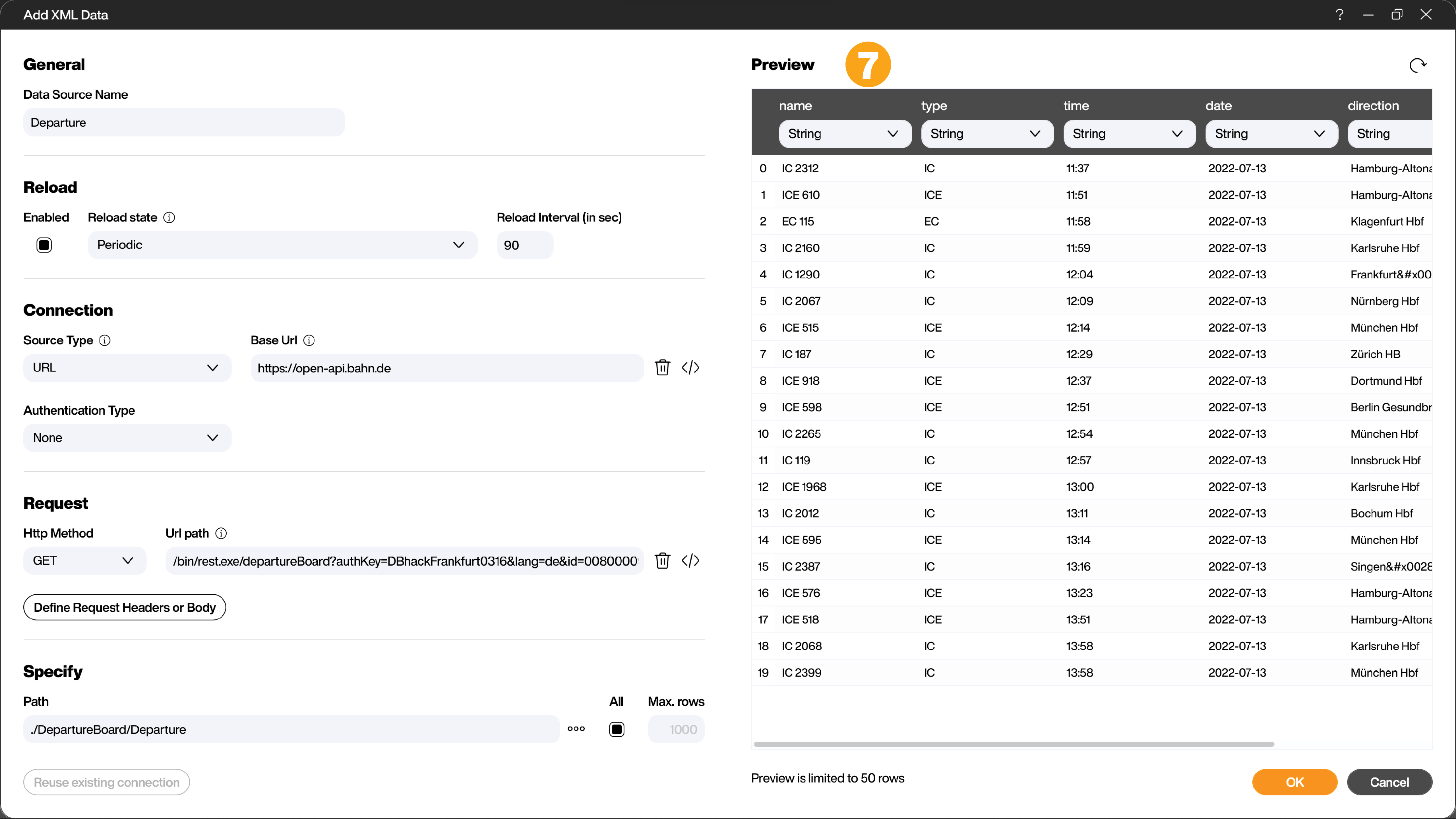
Open the Peakboard Designer and select the data source [XML] under [Add Data Source] (1).
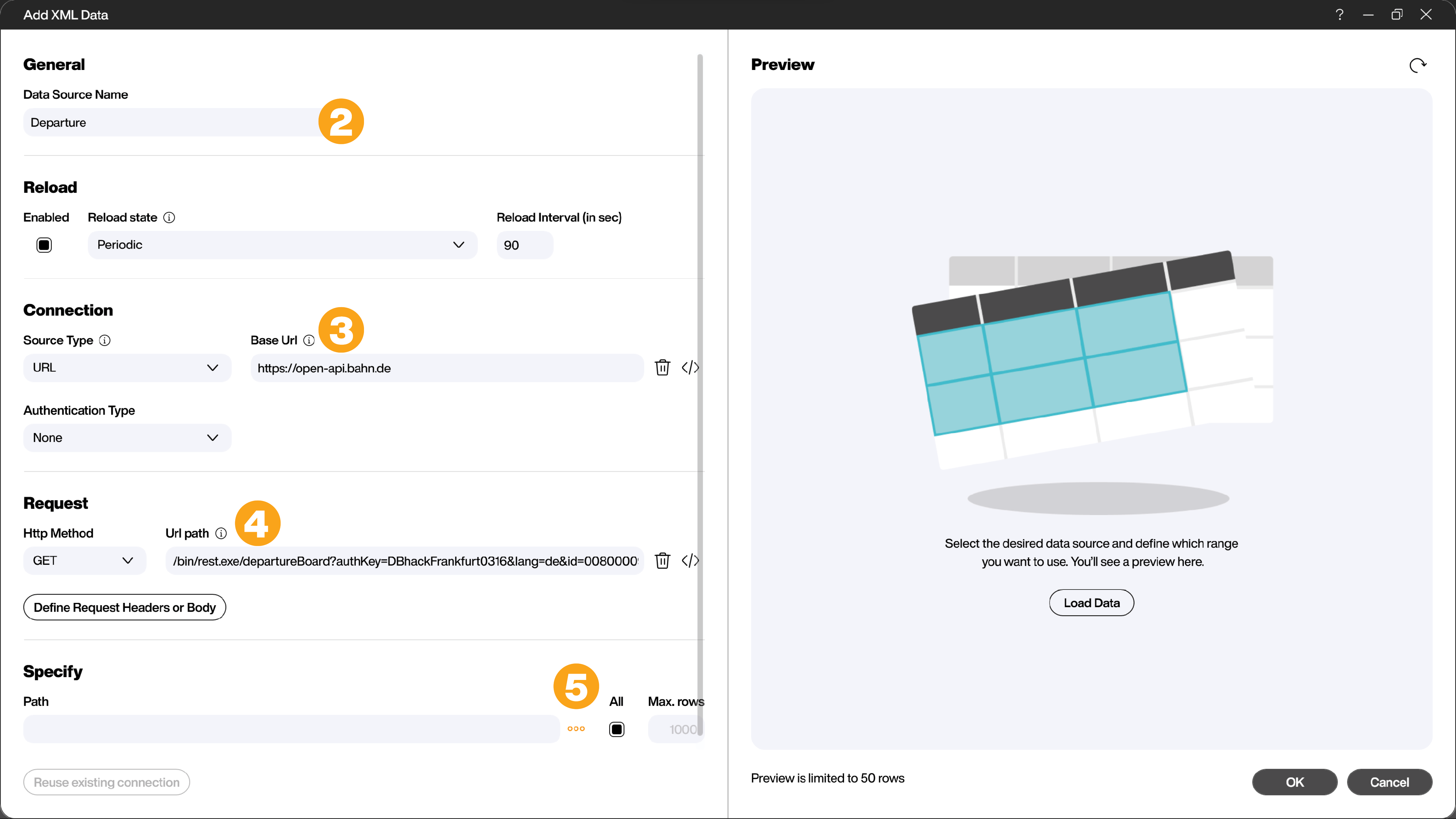
In the XML data source configuration dialog, you must first assign a unique name for the data source (e.g., Departure) (2) and then copy and paste the URL from above into the [Base Url] field (3). Peakboard will automatically split the URL (4). By clicking on the three dots in the [Specify] area (5), you can select the desired elements of the XML file.
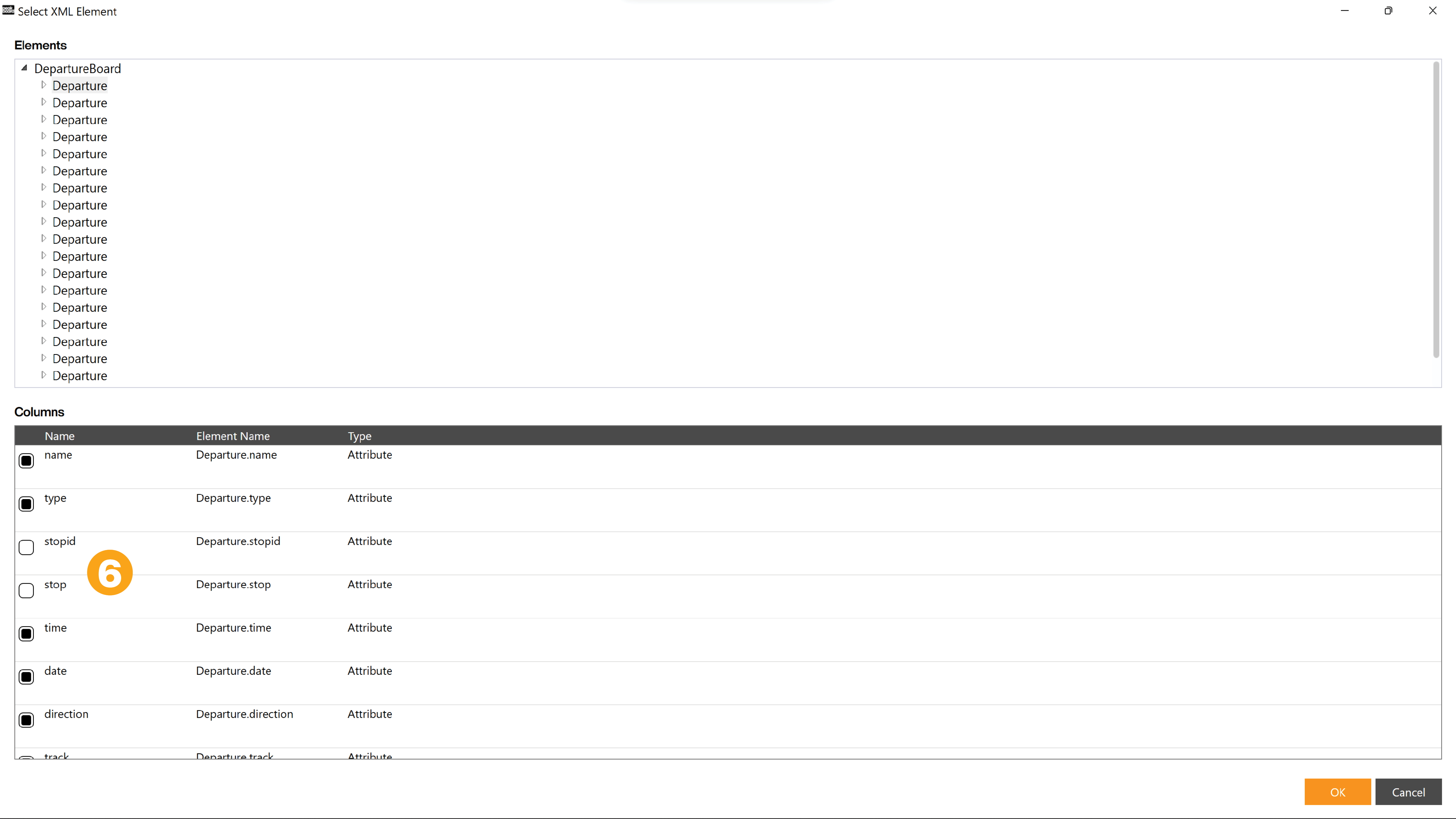
Certain elements are not needed. You can remove the marker here (6), so that they do not appear in the further process. Especially with very complex XML files, it is advisable to discard all elements for which you have no use early on.
Clicking OK transfers all values to the data source dialog. You can check the correct configuration by clicking on [Load Data]. In the Preview area (7), you can also briefly check the plausibility of the data again.
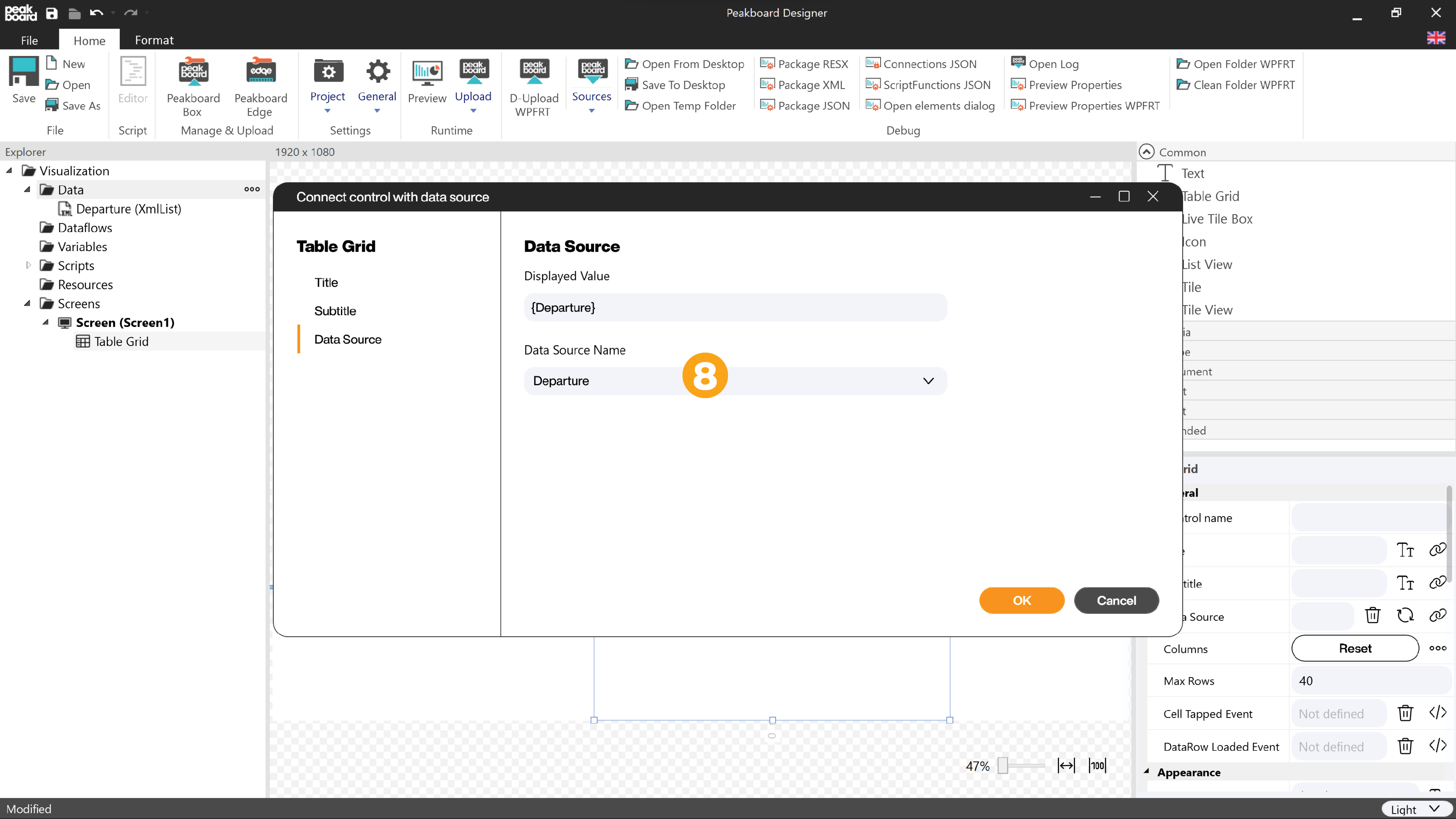
Next, you create the visualization. The data should simply be displayed in a table. To do this, drag a table grid control from the toolbox to the workspace and select the data source created in the previous steps (8).
Confirm by clicking [OK] and adjust the size of the table element by clicking and dragging its edges to fill almost the entire area (9).
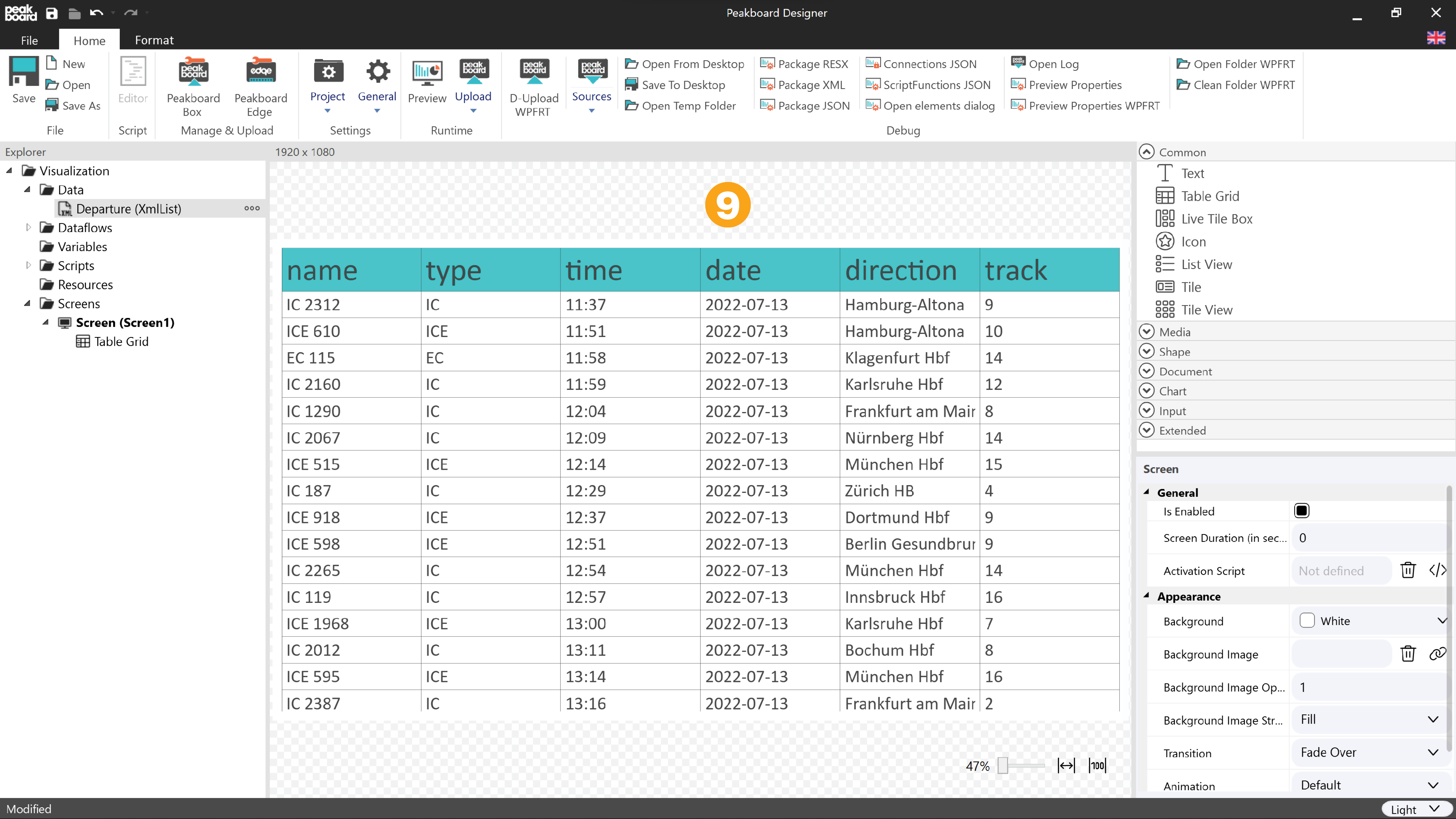
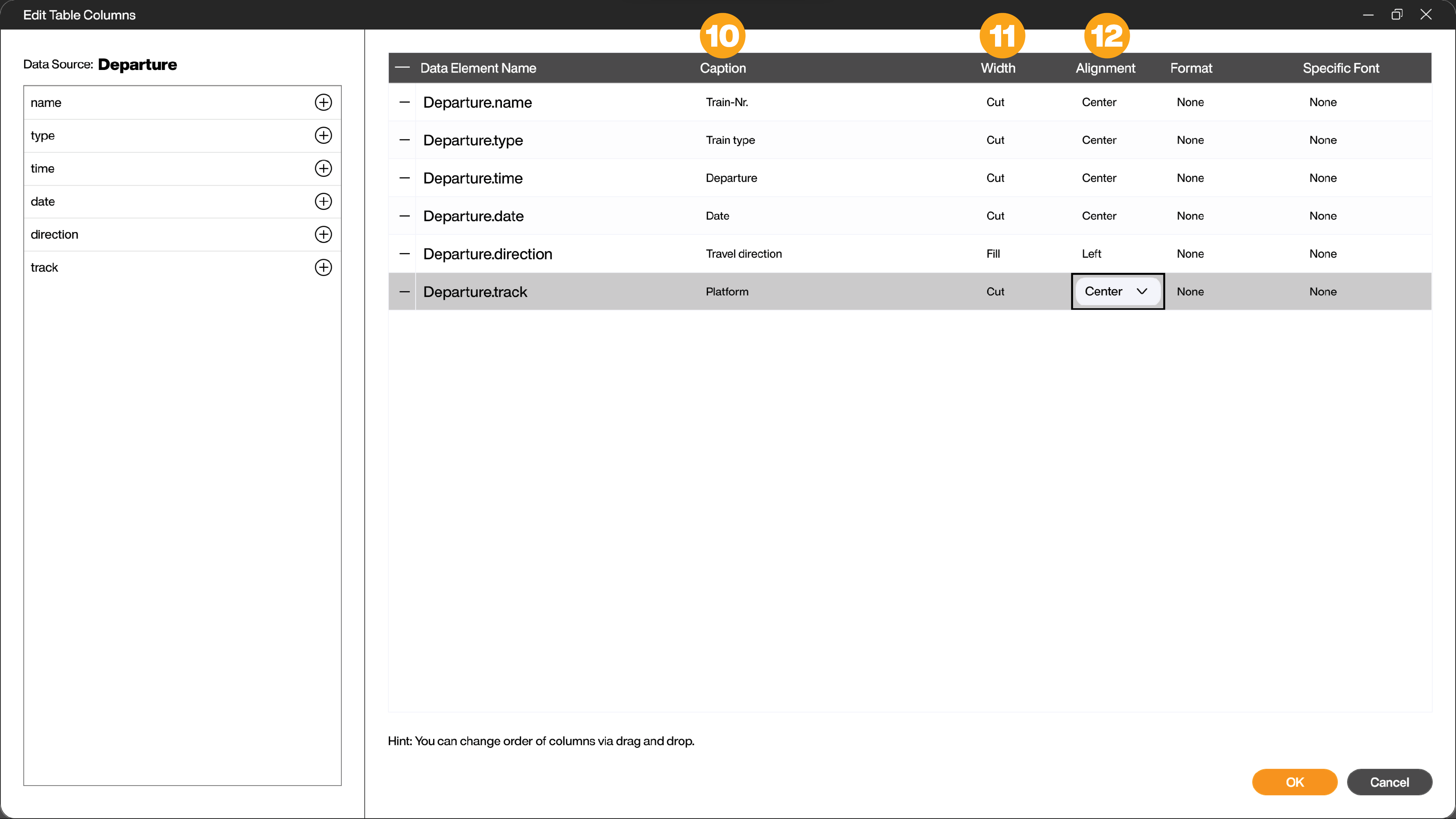
The table element already shows all columns of the data source on the panel. However, it is not very pretty yet. Open the following configuration dialog by clicking on the three dots in the [General] - [Columns] area. All columns of the data source are listed there.
In the column [Caption] (10) give the columns better names, e.g. “Train type” instead of “type” or “Departure” instead of “time” and so on. The column [Width] (11) contains “Fill” by default. Change all columns except the travel direction to “Cut”. This means that the column will be rendered as wide as the widest data element, i.e. to an optimal width. You can also change the [Alignment] (12) to “Center” everywhere except for the travel dircetion. Then click OK.
Back in the main screen, change the following values in the [Appearance] (13) section of the table, for example:
- Header Font: header2, change font size to 45 and bold.
- Body Font: default, change font size to 30
- Header Background: #FFFFAA00
- Border size: 0
- Cell Padding: 30,15,30,15
Now click on [Preview] (14).
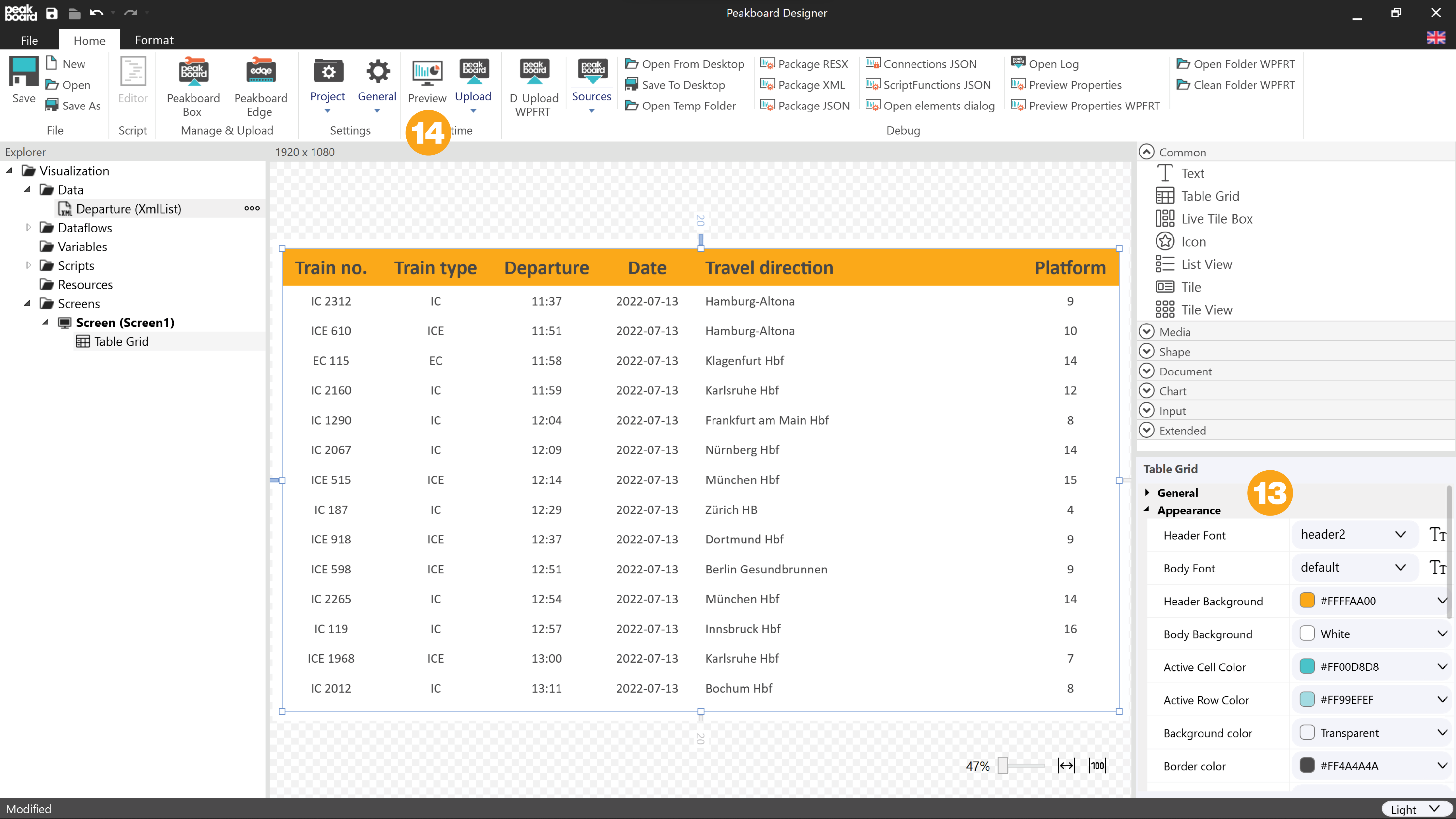
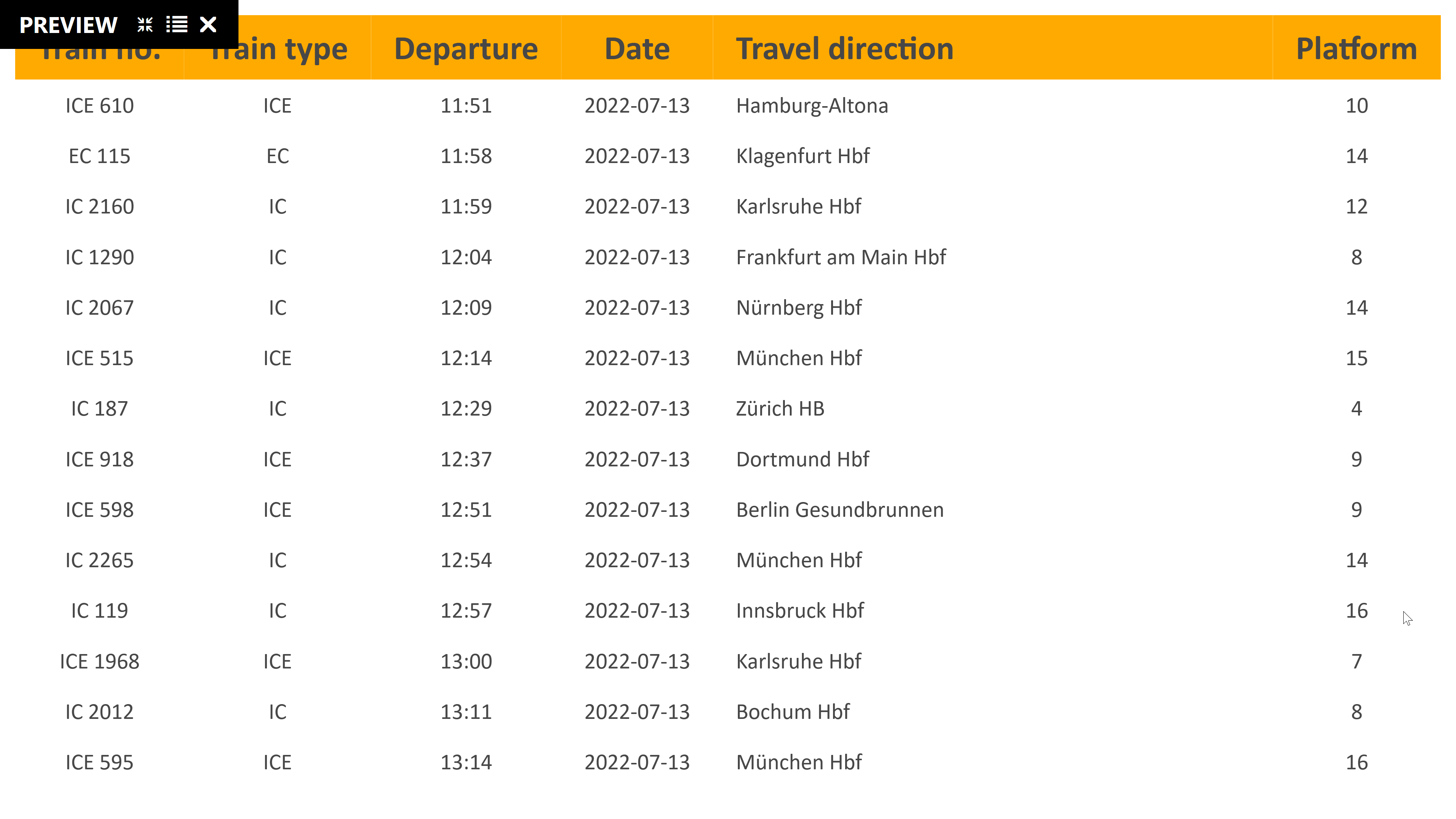
The result should now look something like the screenshot below. The table is filled dynamically and refreshed every 90 seconds according to the information in the data source.